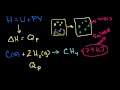
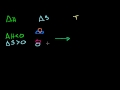
Lec 84 - Enthalpy
Enthalpy Understanding why enthalpy can be viewed as "heat content" in a constant pressure system.
Video is embedded from external source so embedding is not available.
Video is embedded from external source so download is not available.
Channels: Chemistry (General)
Tags: Enthalpy
Uploaded by: khanchemistry ( Send Message ) on 10-09-2012.
Duration: 15m 7s
Here is the next lecture for this course
Chemical Reactions- Changes in Enthalpy
08:20 | 6102 viewsKey Concepts of Heat and Enthalpy
08:41 | 6605 viewsLec 86 - Hess's Law and Reaction Enthalpy ...
15:40 | 3472 viewsLec 114 - Standard Enthalpy of Formation
01:32 | 3021 viewsLec 115 - Standard Enthalpy of Change
02:04 | 2013 viewsChemical Science - Bond Energies / Bond E ...
47:24 | 27654 viewsExpansion and Compression of Gases
10:01 | 6354 viewsLec 4 - MIT 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetic ...
54:37 | 3233 viewsChemical Science - Free Energy of Formati ...
47:47 | 20258 viewsSolutions: Endothermic and Exothermic Rea ...
08:30 | 10964 viewsExothermic Reaction Molten Magic
00:36 | 9798 viewsHow Endothermic Reacts
03:06 | 8586 viewsLec 85 - Heat of Formation
12:35 | 3497 viewsLec 87 - Gibbs Free Energy and Spontaneity
17:40 | 3720 viewsLec 104 - Change of State Example
07:38 | 2224 viewsNo content is added to this lecture.
This video is a part of a lecture series from of khan
Lecture list for this course
Lec 2 - Introduction to the atom
Lec 4 - More on orbitals and electron configuration
Lec 5 - Electron Configurations
Lec 6 - Electron Configurations 2
Lec 8 - Groups of the Periodic Table
Lec 9 - Periodic Table Trends: Ionization Energy
Lec 10 - Other Periodic Table Trends
Lec 11 - Ionic, Covalent, and Metallic Bonds
Lec 12 - Molecular and Empirical Formulas
Lec 13 - The Mole and Avogadro's Number
Lec 14 - Formula from Mass Composition
Lec 15 - Another mass composition problem
Lec 16 - Balancing Chemical Equations
Lec 18 - Stoichiometry: Limiting Reagent
Lec 19 - Ideal Gas Equation: PV=nRT
Lec 20 - Ideal Gas Equation Example 1
Lec 21 - Ideal Gas Equation Example 2
Lec 22 - Ideal Gas Equation Example 3
Lec 26 - States of Matter Follow-Up
Lec 27 - Specific Heat, Heat of Fusion and Vaporization
Lec 28 - Chilling Water Problem
Lec 31 - Covalent Networks, Metallic, and Ionic Crystals
Lec 33 - Suspensions, Colloids and Solutions
Lec 35 - Boiling Point Elevation and Freezing Point Supression
Lec 36 - Introduction to Kinetics
Lec 37 - Reactions in Equilibrium
Lec 38 - Mini-Video on Ion Size
Lec 39 - Keq Intuition (mathy and not necessary to progress)
Lec 40 - Keq derivation intuition (can skip; bit mathy)
Lec 41 - Heterogenous Equilibrium
Lec 42 - Le Chatelier's Principle
Lec 43 - Introduction to pH, pOH, and pKw
Lec 44 - Acid Base Introduction
Lec 45 - pH, pOH of Strong Acids and Bases
Lec 48 - Conjugate Acids and Bases
Lec 49 - pKa and pKb Relationship
Lec 50 - Buffers and Hendersen-Hasselbalch
Lec 51 - Strong Acid Titration
Lec 53 - Half Equivalence Point
Lec 55 - Introduction to Oxidation States
Lec 56 - More on Oxidation States
Lec 57 - Hydrogen Peroxide Correction
Lec 62- Exponential Decay Formula Proof (can skip, involves Calculus)
Lec 63 - Introduction to Exponential Decay
Lec 64 - More Exponential Decay Examples
Lec 65 - Macrostates and Microstates
Lec 66 - Quasistatic and Reversible Processes
Lec 67 - First Law of Thermodynamics/ Internal Energy
Lec 68 - More on Internal Energy
Lec 70 - PV-diagrams and Expansion Work
Lec 71 - Proof: U=(3/2)PV or U=(3/2)nRT
Lec 72 - Work Done by Isothermic Process
Lec 73 - Carnot Cycle and Carnot Engine
Lec 74 - Proof: Volume Ratios in a Carnot Cycle
Lec 75 - Proof: S (or Entropy) is a valid state variable
Lec 76 - Thermodynamic Entropy Definition Clarification
Lec 77 - Reconciling Thermodynamic and State Definitions of Entropy
Lec 81 - Efficiency of a Carnot Engine
Lec 82 - Carnot Efficiency 2: Reversing the Cycle
Lec 83 - Carnot Efficiency 3: Proving that it is the most efficient
Lec 86 - Hess's Law and Reaction Enthalpy Change
Lec 87 - Gibbs Free Energy and Spontaneity
Lec 88 - Gibbs Free Energy Example
Lec 89 - More rigorous Gibbs Free Energy/ Spontaneity Relationship
Lec 90 - A look at a seductive but wrong Gibbs/Spontaneity Proof
Lec 91 - Stoichiometry Example Problem 1
Lec 92 - Stoichiometry Example Problem 2
Lec 93 - Limiting Reactant Example Problem 1
Lec 94 - Empirical and Molecular Formulas from Stoichiometry
Lec 95 - Example of Finding Reactant Empirical Formula
Lec 96 - Stoichiometry of a Reaction in Solution
Lec 97 - Another Stoichiometry Example in a Solution
Lec 98 - Molecular and Empirical Forumlas from Percent Composition