Lec 17 - Renal Physiology (cont.)
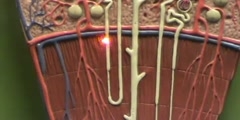
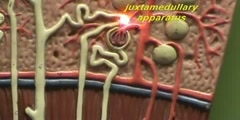
"Lec 17 - Renal Physiology (cont.)" Frontiers of Biomedical Engineering (BENG 100) Professor Saltzman continues his description of nephron anatomy, and the specific role of each part of the nephron in establishing concentration gradients to help in secretion and reabsorption of water, ions, nutrients and wastes. A number of molecular transport processes that produces urine from the initial ultra-filtrate, such as passive diffusion by concentration difference, osmosis, and active transport with sodium-potassium ATPase, are listed. Next, Professor Saltzman describes a method to measure glomerular filtration rate (GFR) using tracer molecule, inulin. He then talks about regulation of sodium, an important ion for cell signaling in the body, as an example to demonstrate the different ways in which nephrons maintain homeostasis. 00:00 - Chapter 1. Introduction 03:06 - Chapter 2. The Role of the Nephron in Ion Balance 16:54 - Chapter 3. The Glomerular Filtration Rate 26:21 - Chapter 4. Selective Reabsorption 39:51 - Chapter 5. Water Balance and Conclusion Complete course materials are available at the Open Yale Courses website: http://open.yale.edu/courses This course was recorded in Spring 2008.
Video is embedded from external source so embedding is not available.
Video is embedded from external source so download is not available.
Channels: Others
Tags: Bowman's capsule glomerular filtration rate homeostasis inulin loop Henle nephron osmosis sodium tubule ultra-filtrate
Uploaded by: yalefrontbio ( Send Message ) on 31-08-2012.
Duration: 44m 37s
Here is the next lecture for this course
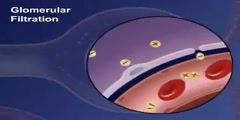
Glomerular Filtration
02:00 | 72415 viewsLec 16 - Renal Physiology
51:14 | 6949 viewsRenal Lobe Model - Cortical Nephron
02:28 | 11101 viewsRenal Corpuscle Model - Renal Capsule
03:01 | 8024 viewsRenal Lobe Model - Juxtaglomerular Nephron
02:52 | 14485 viewsGlomerular Filtration in Kidney Video
00:38 | 28878 viewsLec 14 - Cardiovascular Physiology (cont.)
39:46 | 4880 viewsLec 15 - Cardiovascular Physiology (cont.)
46:08 | 4875 viewsLec 2 - What Is Biomedical Engineering? ( ...
43:47 | 3306 viewsLec 18 - Introduction to Chemical Engineering
54:40 | 3361 viewsFunction of the Nephron
02:32 | 25262 viewsNephron Function
02:31 | 78502 viewsRenal Corpuscle Model - Tubular & Vascula ...
03:05 | 7069 viewsRenal Lobe Model - Cortex & Medulla
02:53 | 7628 viewsLec 4 - Newton's Laws (cont.) and Incline ...
01:07:25 | 4699 viewsNo content is added to this lecture.
This video is a part of a lecture series from of Yale
Lecture list for this course
Lec 1 - What Is Biomedical Engineering?
Lec 2 - What Is Biomedical Engineering? (cont.)
Lec 4 - Genetic Engineering (cont.)
Lec 5 - Cell Culture Engineering
Lec 6 - Cell Culture Engineering (cont.)
Lec 7 - Cell Communication and Immunology
Lec 8 - Cell Communication and Immunology (cont.)
Lec 9 - Biomolecular Engineering: Engineering of Immunity
Lec 10 - Biomolecular Engineering: Engineering of Immunity (cont.)
Lec 11 - Biomolecular Engineering: General Concepts
Lec 12 - Biomolecular Engineering: General Concepts (cont.)
Lec 13 - Cardiovascular Physiology
Lec 14 - Cardiovascular Physiology (cont.)
Lec 15 - Cardiovascular Physiology (cont.)
Lec 18 - Biomechanics and Orthopedics
Lec 19 - Biomechanics and Orthopedics (cont.)
Lec 23 - Tissue Engineering (cont.)