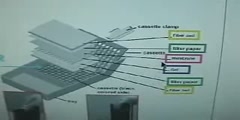
Western blot
The western blot (alternatively, immunoblot) is an analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a given sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide (denaturing conditions) or by the 3-D structure of the protein (native/ non-denaturing conditions). The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are probed (detected) using antibodies specific to the target protein.[1] [2] There are now many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins[3]. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, biochemistry, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. Other related techniques include using antibodies to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The method originated from the laboratory of George Stark at Stanford. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette[4] and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blotting and the detection of post-translational modification of protein is termed Eastern blotting.
Channels: Cell Biology Molecular Biology
Uploaded by: mnazirokur ( Send Message ) on 29-03-2009.
Duration: 2m 35s