Insulin Resistance video
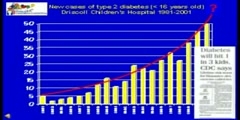
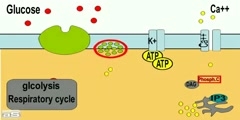
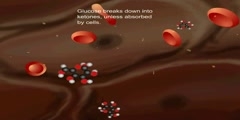
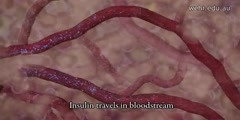
Insulin Resistance. Insulin resistance (IR) is a physiological condition where the natural hormone, insulin, becomes less effective at lowering blood sugars. The resulting increase in blood glucose may raise levels outside the normal range and cause adverse health effects. Certain cell types such as fat and muscle cells require insulin to absorb glucose. When these cells fail to respond adequately to circulating insulin, blood glucose levels rise. The liver helps regulate glucose levels by reducing its secretion of glucose in the presence of insulin. This normal reduction in the liver’s glucose production may not occur in people with insulin resistance. Read more: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_resistance
Channels: Cell Biology Molecular Biology
Tags: Insulin Resistance
Uploaded by: dnasign ( Send Message ) on 24-11-2010.
Duration: 0m 46s