Lec 69 - Acid Chloride Formation
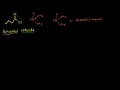
Acid Chloride Formation Acetic Acid to Acetyl Chloride mechanism. Can be generalized to forming any acid halide from a carboxylic acid
Video is embedded from external source so embedding is not available.
Video is embedded from external source so download is not available.
Channels: Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by: khanorganicchem ( Send Message ) on 17-09-2012.
Duration: 11m 49s
Here is the next lecture for this course
Lec 72 - Amide Formation from Acyl Chloride
09:01 | 3140 viewsLec 105 - Chloride Formation (Quiz)
04:38 | 2218 viewsFatty Acid Vesicle Formation
00:37 | 17766 viewsHYDROCHLORIC ACID from SALT
01:39 | 11973 viewsFatty Acid Formation in a Geyser
00:56 | 11521 viewsFloods Supply Sediments for Fossil Formation
02:42 | 5011 viewsVideo lecture: acid-base equilibrium
50:05 | 18754 viewsLecture on acid-base equilibrium part 2
48:13 | 7445 viewsLecture on acid base titration
50:04 | 21942 viewsBlastocyst Formation
00:28 | 12439 viewsNurseReview.Org - Animation on Acid Base ...
00:27 | 24074 viewsTricarboxylic Acid Cycle
07:57 | 32120 viewsCitric Acid Cycle or Krebs Cycle
00:00 | 14119 viewsPalmitic Acid
00:30 | 11555 viewsSp Formation Video
00:11 | 6335 viewsNo content is added to this lecture.
This video is a part of a lecture series from of khan