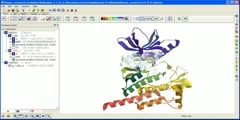
To Correct Mismatches: MutS Binding to a G:T Mismatch
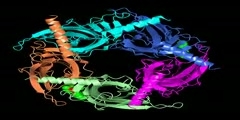
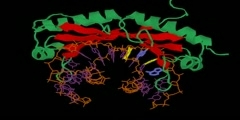
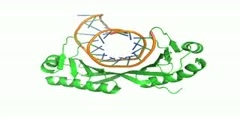
Mismatched base pairs in newly replicated DNA are corrected by an ingenious mechanism of mismatch excision repair. The first step of mismatch recognition is carried out by a dimer of MutS protein. Intriguingly, two polypeptides (normal and darker ones) forming two tunnels to place DNA strands show asymmetrical binding (1E3M.pdb, Obmolova et al. Nature vol. 407, 703).