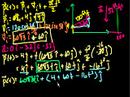Lec 69 - Unit Vector Notation (part 2)
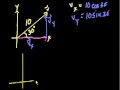
Unit Vector Notation (part 2) More on unit vector notation. Showing that adding the x and y components of two vectors is equivalent to adding the vectors visually using the head-to-tail method
Video is embedded from external source so embedding is not available.
Video is embedded from external source so download is not available.
Channels: Physics (General)
Tags: Unit Vector Notation (part 2)
Uploaded by: khanphysics ( Send Message ) on 08-09-2012.
Duration: 9m 13s
Here is the next lecture for this course
Lec 68 - Unit Vector Notation
09:54 | 3902 viewsLec 137 - Calculating dot and cross produ ...
09:46 | 3908 viewsLec 32 - Unit Vectors and Engineering Not ...
07:58 | 3721 viewsLec 186 - Constructing a unit normal vect ...
10:08 | 4202 viewsLec 187 - Constructing a unit normal vec ...
00:00 | 3166 viewsLec 191 - Surface Integral Example Part 1 ...
11:05 | 3355 viewsLec 200 - Constructing a unit normal vect ...
06:23 | 3223 viewsLec 71 - Projectile Motion with Unit Vect ...
09:14 | 3833 viewsLec - 1 Singapore Math: Grade 3a, Unit 1 ...
15:31 | 2642 viewsLec - 2 Singapore Math: Grade 3a Unit 1 ( ...
15:11 | 2537 viewsLec -3 Singapore Math: Grade 3a, Unit 1 ( ...
13:17 | 2513 viewsLec -4 Singapore Math: Grade 3a, Unit 1 ( ...
12:23 | 2676 viewsLec - 5 Singapore Math: Grade 3a, Unit 1 ...
13:07 | 2375 viewsLec - 6 Singapore Math: Grade 3a, Unit 1 ...
15:43 | 2397 viewsLec - 7 Singapore Math: Grade 3a, Unit 1 ...
13:05 | 2551 viewsNo content is added to this lecture.
This video is a part of a lecture series from of khan
Lecture list for this course
Lec 1 - Introduction to Vectors and Scalars
Lec 2 - Calculating Average Velocity or Speed
Lec 4 - Displacement from Time and Velocity Example
Lec 6 - Newton's First Law of Motion
Lec 7 - Newton's Second Law of Motion
Lec 8 - Newton's Third Law of Motion
Lec 9 - Airbus A380 Take-off Time
Lec 10 - Airbus A380 Take-off Distance
Lec 11 - Why Distance is Area under Velocity-Time Line
Lec 12 - Average Velocity for Constant Acceleration
Lec 13 - Acceleration of Aircraft Carrier Takeoff
Lec 14 - Race Cars with Constant Speed Around Curve
Lec 15 - Introduction to Gravity
Lec 16 - Mass and Weight Clarification
Lec 17 - Gravity for Astronauts in Orbit
Lec 18 - Would a Brick or Feather Fall Faster
Lec 19 - Deriving Displacement as a Function of Time, Acceleration and Initial Velocity
Lec 20 - Plotting Projectile Displacement, Acceleration, and Velocity
Lec 21 - Projectile Height Given Time
Lec 22 - Deriving Max Projectile Displacement Given Time
Lec 23 - Impact Velocity From Given Height
Lec 24 - Visualizing Vectors in 2 Dimensions
Lec 25 - Projectile at an Angle
Lec 26 - Different Way to Determine Time in Air
Lec 27 - Launching and Landing on Different Elevations
Lec 28 - Total Displacement for Projectile
Lec 29 - Total Final Velocity for Projectile
Lec 30 - Correction to Total Final Velocity for Projectile
Lec 31 - Projectile on an Incline
Lec 32 - Unit Vectors and Engineering Notation
Lec 33 - Clearing the Green Monster at Fenway
Lec 34 - Green Monster at Fenway Part 2
Lec 35 - Optimal angle for a projectile part 1
Lec 36 - Optimal angle for a projectile part 2 - Hangtime
How to Find the Optimal Angle for a Projectile Using Calculus Part 4
Lec 39 - Normal Force and Contact Force
Lec 40 - Normal Force in an Elevator
Lec 41 - IInclined Plane Force Componentsnclined Plane Force Components
Lec 42 - Ice Accelerating Down an Incline
Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary
Lec 44 - Correction to Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary
Lec 45 - Force of Friction Keeping Velocity Constant
Lec 46 - Intuition on Static and Kinetic Friction Comparisons
Lec 47 - Static and Kinetic Friction Example
Lec 48 - Introduction to Tension
Lec 50 - Tension in an accelerating system and pie in the face
Lec 51 - Moving pulley problem (part 1)
Lec 52 - Moving pulley problem (part 2)
Lec 53 - Introduction to Momentum
Lec 54 - Momentum: Ice skater throws a ball
Lec 55 - 2-dimensional momentum problem
Lec 56 - 2-dimensional momentum problem (part 2)
Lec 57 - Introduction to work and energy
Lec 58 - Work and Energy (part 2)
Lec 59 - Conservation of Energy
Lec 60 - Work/Energy problem with Friction
Lec 61 - Introduction to mechanical advantage
Lec 62 - Mechanical Advantage (part 2)
Lec 63 - Mechanical Advantage (part 3)
Lec 65 - Introduction to Torque
Lec 70 - Projectile Motion with Unit Vectors
Lec 71 - Projectile Motion with Unit Vectors (part 2)
Lec 72 - Projectile Motion with Ordered Set Notation
Lec 73 - Centripetal Force and Acceleration Intuition
Lec 74 - Visual Understanding of Centripetal Acceleration Formula
Lec 75 - Relationship between angular velocity and speed
Lec 76 - Calculus proof of centripetal acceleration formula
Lec 77 - Loop De Loop Question
Lec 78 - Loop De Loop Answer part 1
Lec 79 - Loop De Loop Answer part 2
Lec 80 - Acceleration Due to Gravity at the Space Station
Lec 81 - Space Station Speed in Orbit
Lec 82 - Conservation of angular momemtum
Lec 83 - Introduction to Newton's Law of Gravitation
Lec 85 - Intro to springs and Hooke's Law
Lec 86 - Potential energy stored in a spring
Lec 87 - Spring potential energy example (mistake in math)
Lec 88 - Introduction to Harmonic Motion
Lec 89 - Harmonic Motion Part 2 (calculus)