PCR - polymerase chain reaction
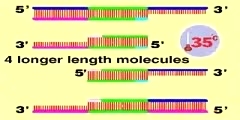
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a biochemistry and molecular biology technique[1] for exponentially amplifying a fragment of DNA, via enzymatic replication, without using a living organism (such as E. coli or yeast). PCR can be used for amplification of a single or few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating millions or more copies of the DNA piece. As PCR is an in vitro technique, it can be performed without restrictions on the form of DNA, and it can be extensively modified to perform a wide array of genetic manipulations. Developed in 1983 by Kary Mullis, PCR is now a common technique used in medical and biological research labs for a variety of tasks, such as the sequencing of genes and the diagnosis of hereditary diseases, the identification of genetic fingerprints (used in forensics and paternity testing), the detection and diagnosis of infectious diseases, and the creation of transgenic organisms. Mullis, who won the Nobel Prize for his work on PCR, credits the psychedelic drug LSD for his invention of the technique. text reff: wikipedia
Channels: Biochemistry Genetics
Tags: pcr
Uploaded by: second ( Send Message ) on 10-09-2007.
Duration: 10m 14s