Mechanism of T7 Primase Helicase
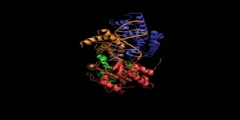
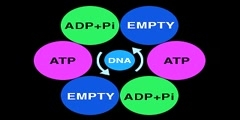
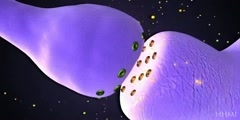
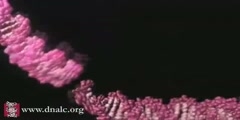
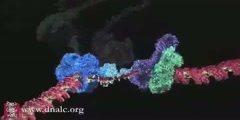
The primase/helicase from the T7 bacteriophage is required for unwinding duplex DNA and the production of short RNA primers called Okazaki fragments during DNA replication. The RNA primers are synthesized in the primase domain of the molecule via a two metal-ion mechanism of catalysis that is facilitated by the zinc-binding domain. During primer synthesis the zinc-binding domain closes over the active site of the primase domain. The helicase domain unwinds DNA by shuttling the 3'-end of the duplex DNA away from the molecule by pulling the 5'-strand through the enzyme. The mechanism of unwinding is facilitated by DNA binding loops present in the helicase domain. This movie is based on the X-ray crystal structure of the primase and helicase domains. Zinc binding domains have been modeled in. The first half of the animation highlights the possible mechanism of DNA unwinding by the helicase domain. The motion of each domain has been inferred from the crystal structure. The second portion of the movie highlights the mechanism of RNA primer synthesis by the primase/zinc binding domain. Synthesis of short RNA primers of a defined sequence (5'-ACCC-3') are utilized by the replicative polymerases during lagging strand DNA synthesis. Finally, the new primer/template is presented to the replication machinery by the zinc binding domain. www.scianafilms.com
Channels: Scientific Animations Genetics
Tags: primase
Uploaded by: sertan ( Send Message ) on 05-01-2008.
Duration: 1m 54s