Histone Deacetylation
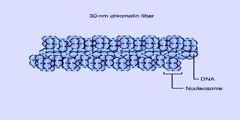
Histone deacetylases (HDAC) (EC number 3.5.1) are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone. Its action is opposite to that of histone acetyltransferase. Deacetylation removes acetyl groups from histone tails, causing the histones to wrap more tightly around the DNA and interfering with the transcription of genes by blocking access by transcription factors. The overall result of histone deacetylation is a global (non specific) reduction in gene expression. Histone Deacetylase involved in a series of pathway in the living system. In Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), they are: Environmental Information Processing; Signal transduction; Notch signaling pathway Cellular Processes; Cell Growth and Death; Cell cycle Human Diseases; Cancers; Chronic myeloid leukemia Histone acetylation plays an important role in regulation of gene expression. Hyperacetylated chromatin is transcriptionally active and hypoacetylated is silent. A study on mice found that a specific subset of mouse genes (7%) was deregulated in the absence of HDAC1. Their study also found a regulatory cross talk between HDAC1 and HDAC2 and suggest a novel function for HDAC1 as a transcriptional coactivator.
Channels: Scientific Animations Biochemistry Genetics
Tags: deacetylation
Uploaded by: tubeman ( Send Message ) on 08-09-2007.
Duration: 3m 18s