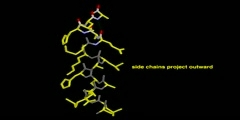
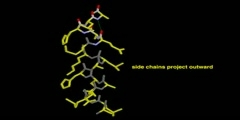
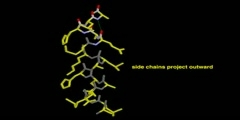
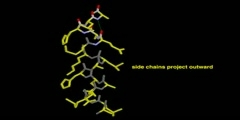
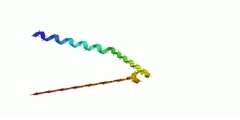
Model of Alpha Helix Structure
A common motive in the secondary structure of proteins, the alpha helix is a right-handed coiled conformation, resembling a spring, in which every backbone donates a hydrogen bond to the backbone of the amino acid four residues earlier (hydrogen bonding).
Channels: Biochemistry
Tags: alphahelix proteomics protein
Uploaded by: okur ( Send Message ) on 27-05-2007.
Duration: 0m 5s