mRNA splicing animation
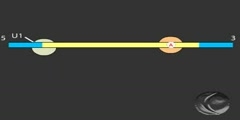
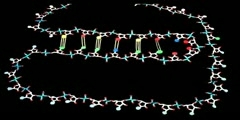
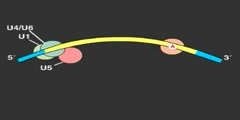
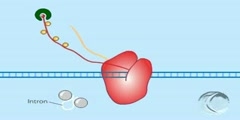
In genetics, splicing is a modification of genetic information after transcription, in which introns of precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) are removed and exons of it are joined. Since in prokaryotic genomes introns do not exist, splicing naturally only occurs in eukaryotes. The splicing prepares the pre-mRNA to produce the mature messenger RNA (mRNA), which then undergoes translation as part of the protein synthesis to produce proteins. Splicing includes a series of biochemical reactions, which are catalyzed by the spliceosome, a complex of small nuclear ribonucleo-proteins (snRNPs).
Channels: Scientific Animations Biochemistry Molecular Genetics
Tags: splicing
Uploaded by: watchme ( Send Message ) on 04-11-2007.
Duration: 2m 55s